This handout photo provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention was taken in 1997 during an investigation into an outbreak of monkeypox, which took place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and depicts the dorsal surfaces of a monkeypox case in a patient who was displaying the appearance of the characteristic rash during its recuperative stage. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said June 3, 2022 it was aware of more than 700 global cases of monkeypox, including 21 in the United States, with investigations now suggesting it is spreading inside the country. (AFP PHOTO / Brian W.J. Mahy, BSc, MA, PhD, ScD, DSc / Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
CEBU CITY, Philippines – Central Visayas remains free of monkeypox, the regional bureau of the Department of Health (DOH-7) announced.
DOH-7, in a press conference on Tuesday, July 26, said that the region, and the entire country for that matter, has no confirmed cases of monkeypox.
Dr. Eugenia Mercedes Cañal, cluster head of the Regional Epidemiological and Surveillance Unit (Resu-7), said they detected two suspected cases of the viral infection in Bohol and Cebu provinces.
Fortunately, the two patients tested negative of the virus that causes monkeypox upon confirmation through laboratory tests.
“We have suspected cases of monkeypox, one in Bohol and one here in Cebu, a week ago. However, all of them are negative,” said Cañal.
Cañal told the media that they received reports from barangay health workers (BHWs) in Bohol that a resident there showed symptoms of the infection.
“We also received information from hospital workers in Cebu that one of their patients also exhibited symptoms. When we conducted further confirmatory tests, they yielded negative results,” she explained.
Monkeypox was recently declared a “public health emergency of international concern” by the World Health Organization (WHO).
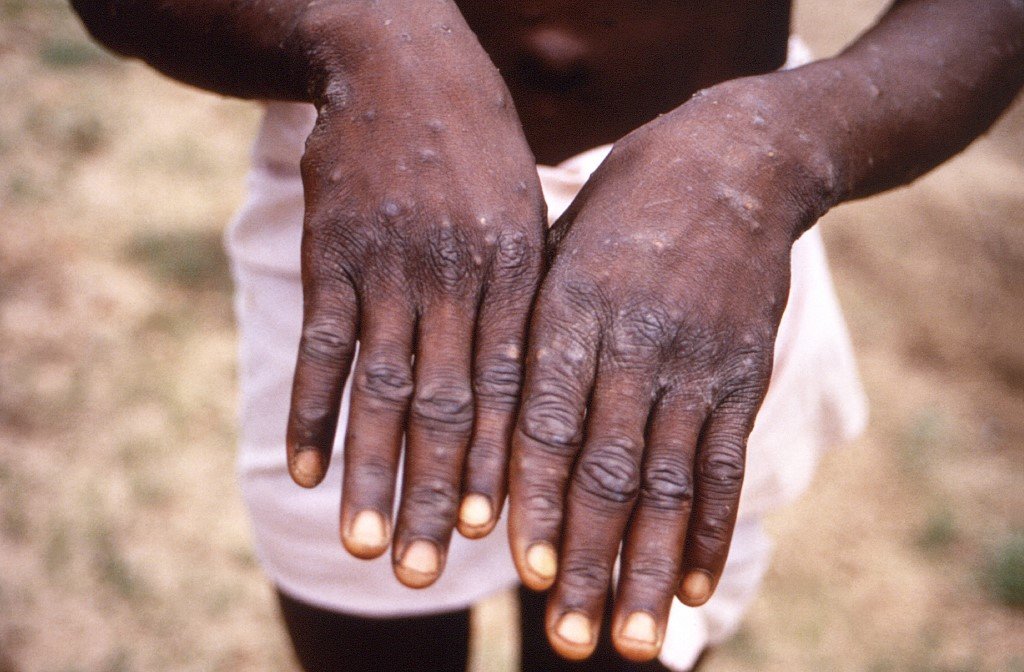
A viral infection resembling smallpox and first detected in humans in 1970, monkeypox is less dangerous and contagious than smallpox, which was eradicated in 1980.
The first symptoms of monkeypox are fever, headaches, muscle pain and back pain during the course of five days.
Rashes subsequently appear on the face, palms of hands and soles of the feet, followed by lesions, spots and finally scabs.
The illness usually lasts two to four weeks.
The virus can spread through direct contact with the infectious rash, scabs or body fluids; respiratory secretions during prolonged, face-to-face contact, or during intimate physical contact, or touching items such as clothing or linen that previously touched the infectious rash or body fluids. / with reports from INQUIRER.net
RELATED STORIES
DOH eyes purchase of vaccines vs monkeypox
Canada reports 10 new cases of monkeypox, including the first in Ontario
Monkeypox outbreak constitutes global health emergency – WHO
/dcb